SHORT WAVE INFRARED HEATING
Targeted heating where it matters
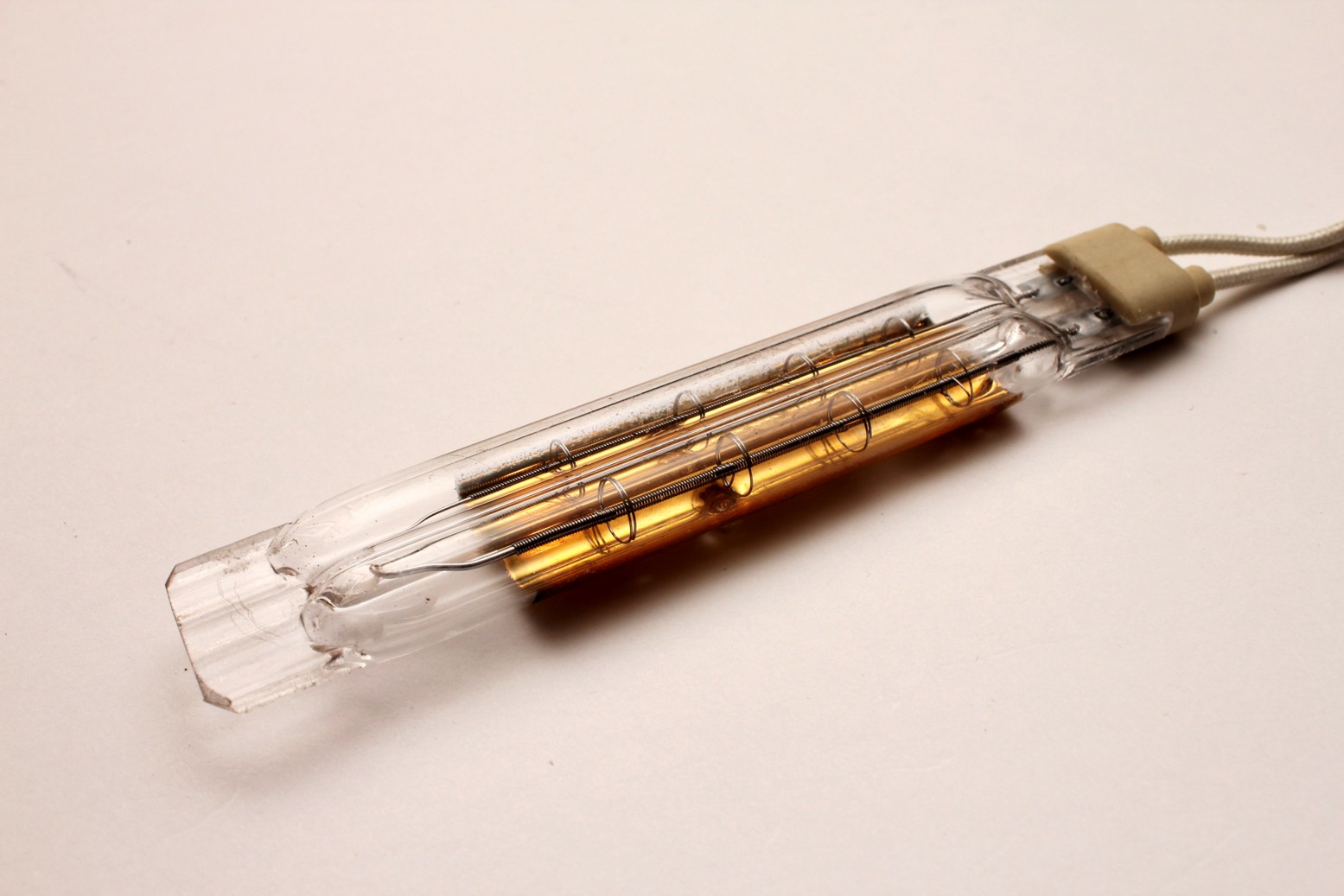
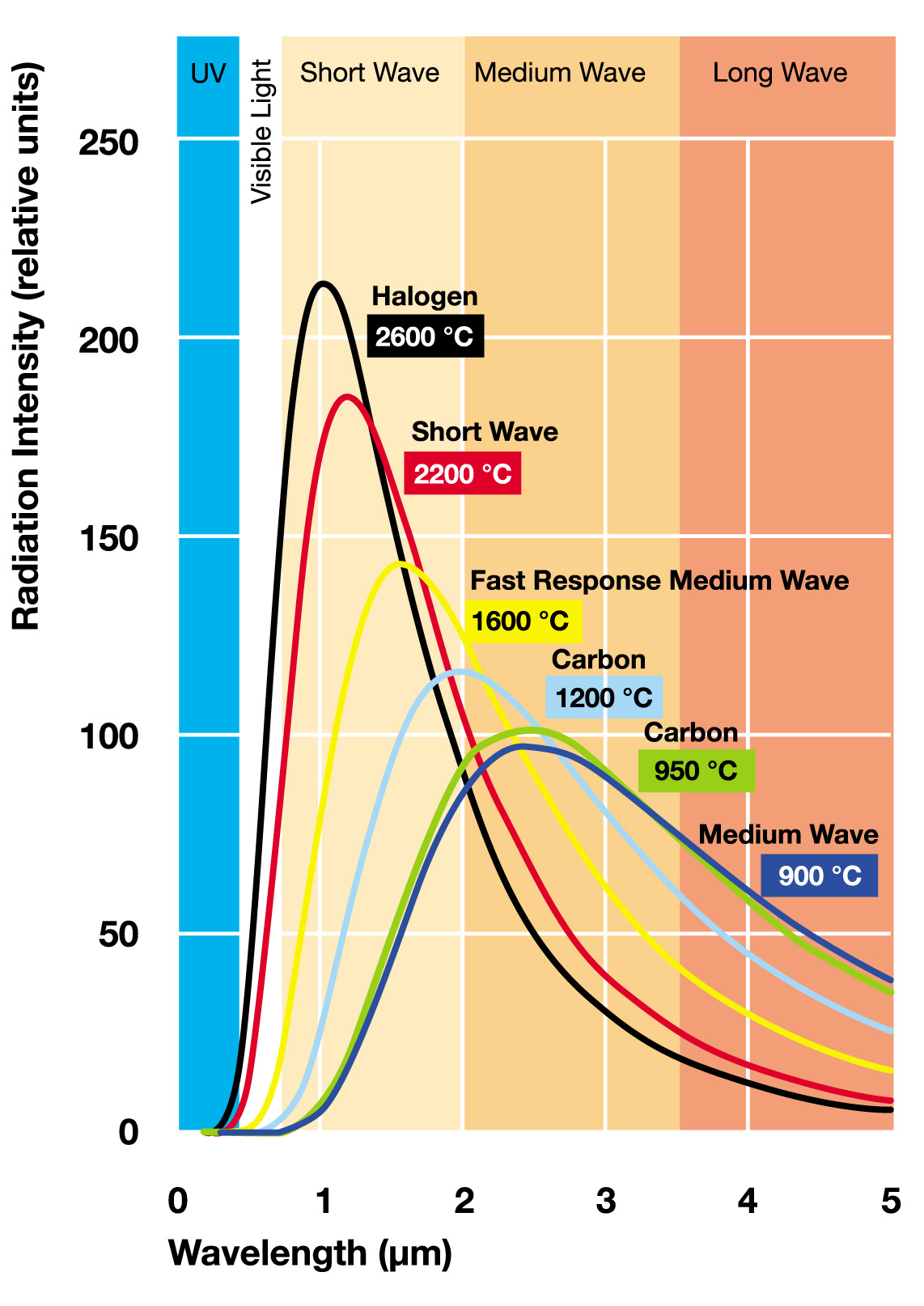
Short wave infrared heating elements, or infrared emitters comprise a linear coiled metal filament surrounded by a clear quartz envelope (tube). The tube is evacuated, with the electrical connections being taken through seals on one or both ends. Short wave infrared refers to that part of the wavelength spectrum of the emitted light. The wavelength emitted of any infrared emitter is in direct relationship to the temperature of the filament: The peak wavelength is directly proportional to the maximum temperature of the filament.This is called Wien’s Law. Short wave emitters deliver large amounts of infrared radiation energy very quickly and instantaneously. Infrared radiation penetrates into the substrate with high efficacy compared to others modes of heating. Short wave emitters are in effect, instant heat. The instantaneous operation of short wave heating elements has several advantages over other forms of heating including substantial power savings, high efficiency of heat delivery, compact installation and low level risk of fire hazards.
POWER SAVINGS
The power savings of a short wave heating system can be substantial compared to convection heating. Short wave infrared lamps have zero warm up time, they are effectively instant heat. A short wave infrared heating is one of the most efficient form of heating, delivering large amounts of energy instantly to where it matters most : onto the product, and no unnecessary heating of the surrounding infrastructure. Because the system has a zero warm up time, it can be switched off during times when there is no product on the line, when there is a breakdown or even when operators go to lunch. Convection systems need hours to reach operating temperature and cannot be switched off without compromising production time.
HIGH EFFICIENCY QUARTZ ENVELOPE
The construction of a short wave infrared heating lamp means that large amounts of heat are delivered quickly, but also with extreme efficiency. Infrared heat is actually light, whereby heat is the result of the product absorbing the infrared light. When we design infrared heating system the properties of light must be considered: absorption, transmission and reflection. Quartz is translucent to IR radiation, which means the quartz envelope of the infrared lamp does not absorb the infrared radiation. About 95% of the power used is emitted onto the product,not in heating up the element. Typical heating elements like stainless steel, silicide, ceramic tiles, 50% of the energy is wasted just heating up the element itself.
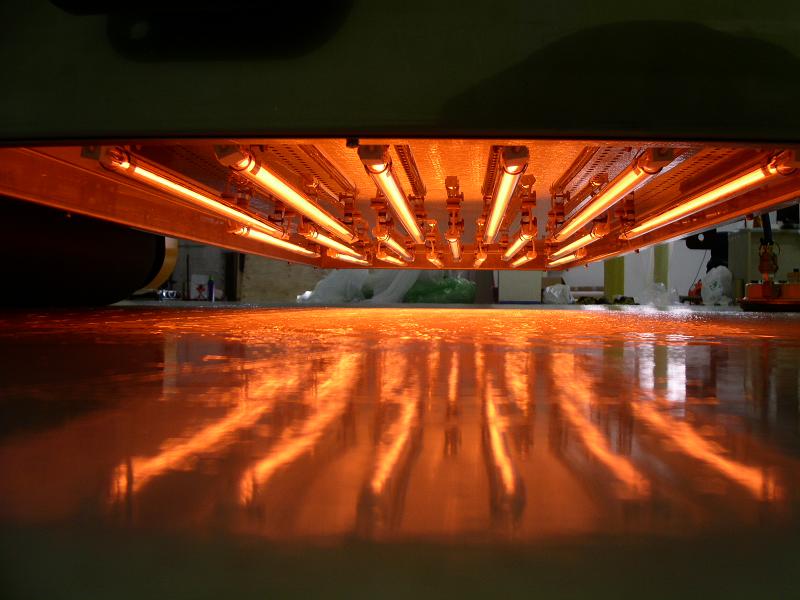
COMPACT INSTALLATION
One of the main advantages of short wave infrared heating is the small size of the installation. Normal convection ovens are often enormous and consume large amounts of valuable space and are very expensive to run an install. For example consider a standard powder coating application: a typical convection oven will be at least 10-20 meters in length. An IR system will less than a meter! In today’s industrial market, factory space comes at a premium. Infrared heating systems are small, compact and easily retrofitted into existing processes. Installation is simple, usually completed within hours, not weeks. Unlike gas convection systems, electric infrared heating requires no maintenance and ongoing compliance is not required. The lifetime of the quartz infrared twin tube, when installed correctly will be in excess of 100000 hours.
SHORT WAVE (NIR) INFRARED LAMP SPECIFICATIONS
-
Twin tube design for stability up to 4 meters continuous length
-
Quartz Section 23×11 or 34×14
-
Peak wavelength between 1.2 and 1.4 microns
-
Linear power density up to 100W/cm
-
Gold reflector standard
-
Standard or custom lengths available
-
Custom wiring configurations